Free Space Radar Level Transmitter
This device is a non-contact radar level transmitter that uses FMCW technology. It measures distance, level and volume of powders, granulates and other solids. It is ideal for measuring the level of solids in applications with very dusty atmospheres.
Highlights
- 2-wire loop-powered 80 GHz transmitter – HART® 7
- Accuracy: ±2 mm / ±0.08 ̈
- PEEK Lens antenna options include:
- DN70 / 23⁄4 ̈ antenna with 4° beam angle suitable for long nozzles and distances up to 100 m / 328 ft
- DN40 / 11⁄2 ̈ antenna with 8° beam angle, available with 11⁄2 ̈ thread connections, measures up to 30 m / 98 ft
- 112 mm / 4.4 ̈ antenna extension for long nozzles
- One user interface for all applications
- Antenna purging system for flange connection without antenna extension
- Empty tank spectrum function eliminates false reflections caused by tank internals
- Extensive choice of process connections (threaded ≥11⁄2 ̈ and flange ≥DN50 / 2 ̈)
- Extremely high dynamics with considerable signal-to-noise ratio for clear vision in dusty atmospheres
- 4 GHz sweep for high resolution
- Low-cost low-pressure disc flange
- No need for antenna aiming kits. A slanted flange can be installed if necessary.
Industries
- Metals, Minerals & Mining
- Chemical market
- Power
- Agri-food
- Wastewater
- Pulp & Paper
Applications
- Buffer silos
- Buffer silos
- Bulk storage containers or hoppers
Applications
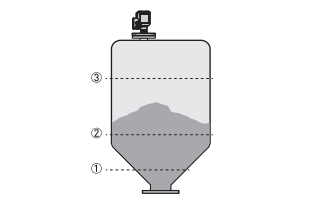
Level measurement of solids
Mass (volume) measurement
Measuring principle
A radar signal is emitted via an antenna, reflected from the product surface and received
after a
time t. The radar principle used is FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave).
The FMCW-radar transmits a high frequency signal whose frequency increases linearly
during
the measurement phase (called the frequency sweep). The signal is emitted, reflected on
the
measuring surface and received with a time delay, t. Delay time, t=2d/c, where d is the
distance
to the product surface and c is the speed of light in the gas above the product.
For further signal processing the difference Δf is calculated from the actual
transmitted
frequency and the received frequency. The difference is directly proportional to the
distance. A
large frequency difference corresponds to a large distance and vice versa. The frequency
difference Δf is transformed via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) into a frequency
spectrum and
then the distance is calculated from the spectrum. The level results from the difference
between
the tank height and the measured distance.
Technical data
Measuring system
| Measuring principle | 2-wire loop-powered level transmitter; FMCW radar |
|---|---|
| Frequency range | W-band (78...82 GHz) |
| Max. radiated power (EIRP) | < -41.3 dBm according to ETSI EN 307 372 (TLPR) and ETSI EN 302 729 (LPR) |
| Application range | Level measurement of powders and granulates |
| Primary measured value | Distance and reflection |
| Secondary measured value | Level, volume and mass |
Design
| Construction | The measurement system consists of a measuring sensor (antenna) and a signal converter |
|---|---|
| Options | |
| Integrated LCD display (-20..+70°C / -4...+158°F); if the ambient temperature is not in these limits, then this condition can stop the display | |
| Distance piece (for process temperature: +150...+200°C / +302...+392°F) | |
| Antenna purging system (supplied with a G 1/4 connection) | |
| Weather protection | |
| Max. measuring range | |
| Lens, DN40 (11⁄2 ̈): 30 m / 98 ft | |
| Lens, DN70 (23⁄4 ̈): 100 m / 328.1 ft | |
| Refer also to "Measuring accuracy" on page 16 | |
| Min. tank height | 1 m / 40 ̈ |
| Recommended minimum blocking distance | 0.3 m / 12 ̈ (add 112 mm / 4.4 ̈ if the DN40 Lens antenna has an antenna extension) |
| Min. distance for reflection measurement | 1 m / 3.3 ft |
| Beam angle (antenna) | |
| Lens, DN40 (11⁄2 ̈): 8° | |
| Lens, DN70 (23⁄4 ̈): 4° |